WshLogger
The logger module for WSH (Windows Script Host) writes logging messages in a console or a file or Windows-Event-Viewer.
tuckn/WshModeJs basic applications structure
WshBasicApps
├─ WshCommander
├─ WshConfigStore (./dist/module.js)
├─ WshDotEnv (./dist/module.js)
├─ WshLogger - This repository (./dist/module.js)
└─ WshModeJs (./dist/bundle.js)
WshBasicApps contains all the above modules.
Operating environment
Works on JScript in Windows.
Installation
(1) Create a directory of your WSH project.
D:\> mkdir MyWshProject
D:\> cd MyWshProject
(2) Download this ZIP and unzip or Use the following git command.
> git clone https://github.com/tuckn/WshLogger.git ./WshModules/WshLogger
or
> git submodule add https://github.com/tuckn/WshLogger.git ./WshModules/WshLogger
(3) Create your JScript (.js) file. For Example,
D:\MyWshProject\
├─ MyScript.js <- Your JScript code will be written in this.
└─ WshModules\
└─ WshLogger\
└─ dist\
└─ bundle.js
I recommend JScript (.js) file encoding to be UTF-8 [BOM, CRLF].
(4) Create your WSF packaging scripts file (.wsf).
D:\MyWshProject\
├─ Run.wsf <- WSH entry file
├─ MyScript.js
└─ WshModules\
└─ WshLogger\
└─ dist\
└─ bundle.js
And you should include .../dist/bundle.js into the WSF file.
For Example, The content of the above Run.wsf is
<package>
<job id = "run">
<script language="JScript" src="./WshModules/WshLogger/dist/bundle.js"></script>
<script language="JScript" src="./MyScript.js"></script>
</job>
</package>
I recommend this WSH file (.wsf) encoding to be UTF-8 [BOM, CRLF].
Awesome! This WSH configuration allows you to use the following functions in JScript (.\MyScript.js).
Usage
Now .\MyScript.js (JScript ) can use Wsh.Logger.
For example.
var logger = Wsh.Logger; // Shorthand
var lggr = logger.create('warn/winEvent'); // Set warn level
lggr.error('1 Error message');
lggr.warn('2 Warning message');
lggr.success('3 Success message');
lggr.info('4 Info message');
lggr.debug('5 Debug message');
logger.transport();
// Creates the new error event into your Windows Event Viewer.
// [2020-07-19T13:11:09] error 1 Error message
// [2020-07-19T13:11:09] warn 2 Warning message
Logging Levels
As shown above, if you specify warn level in the create argument, the success, info, and debug defined in the code are not recorded as logs.
The hierarchy of logging levels is as follows in Highest to Lowest order:
- off
- error
- warn
- success
- info
- debug
For example, if you specify off, a log is not recorded.
Output Console
var logger = Wsh.Logger; // Shorthand
var lggr = logger.create('info/console');
// Specified `console`, it works like console.log.
lggr.error('1 Error message'); // console.error
lggr.warn('2 Warning message'); // console.log
lggr.success('3 Success message'); // console.log
lggr.info('4 Info message'); // console.log
lggr.debug('5 Debug message');
> cscript .\Run.wsf
[2020-07-19T13:11:09] error 1 Error message
[2020-07-19T13:11:09] warn 2 Warning message
[2020-07-19T13:11:09] success 3 Success message
[2020-07-19T13:11:09] info 4 Info message
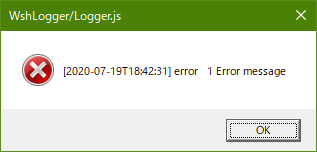
Output Popup Window
var logger = Wsh.Logger; // Shorthand
var lggr = logger.create('error/popup');
lggr.error('1 Error message');
lggr.warn('2 Warning message');
lggr.success('3 Success message');
lggr.info('4 Info message');
lggr.debug('5 Debug message');
logger.transport();
Output File
var logger = Wsh.Logger; // Shorthand
var lggr = logger.create('success/D:\\logs\\foo_#{yyyy-MM-dd}.log');
lggr.error('1 Error message');
lggr.warn('2 Warning message');
lggr.success('3 Success message');
lggr.info('4 Info message');
lggr.debug('5 Debug message');
logger.transport();
Writes the logs into D:\logs\foo_2020-07-19.log.
[2020-07-19T13:11:09] error 1 Error message
[2020-07-19T13:11:09] warn 2 Warning message
[2020-07-19T13:11:09] success 3 Success message
If you omit the directory path, for example, 'warn/foo_#{yyyy-MM-dd}.log', the %CD% (Current Working Directory) will be applied.
No Logging
var logger = Wsh.Logger; // Shorthand
var lggr = logger.create('off');
lggr.error('1 Error message');
lggr.warn('2 Warning message');
lggr.success('3 Success message');
lggr.info('4 Info message');
lggr.debug('5 Debug message');
logger.transport(); // Non logging
Together with another WshModeJs Apps
If you want to use it together with other WshModeJs Apps, install as following
> git clone https://github.com/tuckn/WshModeJs.git ./WshModules/WshModeJs
> git clone https://github.com/tuckn/WshCommander.git ./WshModules/WshCommander
> git clone https://github.com/tuckn/WshLogger.git ./WshModules/WshLogger
or
> git submodule add https://github.com/tuckn/WshModeJs.git ./WshModules/WshModeJs
> git submodule add https://github.com/tuckn/WshCommander.git ./WshModules/WshCommander
> git submodule add https://github.com/tuckn/WshLogger.git ./WshModules/WshLogger
The definition in the WSF packaging scripts file (.wsf) is as follows.
<package>
<job id = "run">
<script language="JScript" src="./WshModules/WshModeJs/dist/bundle.js"></script>
<script language="JScript" src="./WshModules/WshCommander/dist/module.js"></script>
<script language="JScript" src="./WshModules/WshLogger/dist/module.js"></script>
<script language="JScript" src="./MyScript.js"></script>
</job>
</package>
Please note the difference between .../dist/bundle.js and .../dist/module.js.
I recommend using WshBasicApps.
That includes all modules.
Dependency Modules
You can also use the following helper functions in your JScript (.\MyScript.js).
- tuckn/WshPolyfill
- tuckn/WshUtil
- tuckn/WshPath
- tuckn/WshOS
- tuckn/WshFileSystem
- tuckn/WshProcess
- tuckn/WshChildProcess
- tuckn/WshNet
- tuckn/WshModeJs
Documentation
See all specifications here and also below.
License
MIT
Copyright (c) 2020 Tuckn